
(a)
Interpretation: The kind of sigmatropic rearrangement that occurs in each of the given reactions has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Pericyclic reactions are “ any concerted reaction in which bonds are formed or brocken in a cyclic transition state”. There is a single transition state from start to finish, in contrast to a stepwise reaction.
There are mainly three types of pericyclic reactions,
- 1) Electrocyclic reactions
- 2) Cycloaddition reactions
- 3) Sigmatropic reactions
In a sigmatropic reaction “ one new sigma-bond is formed as another breaks.”
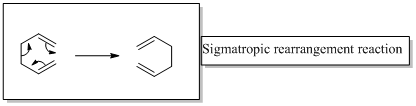
Sigmatropic rearrangement reactions are named with digits. For example a [1, 3] sigmatropic rearrangement describe a reaction in which the residue migrates from position 1 to position 3.
(b)
Interpretation: Using arrows the electron rearrangement takes place in the given reactions has to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Pericyclic reactions are “ any concerted reaction in which bonds are formed or brocken in a cyclic transition state”. There is a single transition state from start to finish, in contrast to a stepwise reaction.
There are mainly three types of pericyclic reactions,
- 1) Electrocyclic reactions
- 2) Cycloaddition reactions
- 3) Sigmatropic reactions
In a sigmatropic reaction “ one new sigma-bond is formed as another breaks.”

Sigmatropic rearrangement reactions are named with digits. For example a [1, 3] sigmatropic rearrangement describe a reaction in which the residue migrates from position 1 to position 3.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What other alkene is also formed along with Y in Sample Problem 9.3 (Attached) ? What alkenes would form from X if no carbocation rearrangement occurred?arrow_forward1.a. Give the product(s) of the reaction below. …...... D H₂, Pd/C Show stereochemistry. Give product(s) for this reaction. No mechanism is necessary. 1.b. Are there multiple products in 1.a.? Are there major and minor product(s)? Explain.arrow_forwardWhy does Hammett Equation only apply to meta and para substituted rings and not others? Explainarrow_forward
- Give the all possible resonance structures of the carbocation for both the o- and m- product and explain why the m-product is formedarrow_forwardComplete the following for the below reaction. i. draw the complete Molecular Orbital diagram with electron filling, nodes and phasing. ii. label each level with the number of bonding and antibonding interactions iii. label each level as bonding, nonbonding or antibonding, and HOMO & LUMO iv. Using the correct level, show how the cyclization occurs to give cyclohexadiene and indicate whether the product is cis or trans. heatarrow_forwardBased on the hydrogenation and the bromination reaction information, how many different alkene structures can you draw that could be Compound X? (If enantiomers are possible, count each pair of enantiomers as one structure.)arrow_forward
- 6.The three compounds below can form a carbocation under aqueous acidic conditions. Draw the structure of Carbocation. || =arrow_forward3. Progesterone is a common female hormone, which is important during the menstrual cycle. The following compound is believed to be an intermediate for a crucial step in the synthesis of progesterone. Why is this intermediate more stable than you would otherwise think for a carbocation? Explain fully (with structures).arrow_forward2. A benzene ring alters the reactivity of a neighboring group in the so-called "benzylic" position, similarly to how a double bond alters the reactivity of groups in the "allylic" position. R .R allylic position benzylic position Benzylic cations, anions, and radicals are all more stable than simple alkyl intermediates. a) Use resonance structures to show the delocalization of the positive charge, negative charge, and unpaired electron of the benzyl cation, anion, and radical.arrow_forward
- a. What is the major monobromination product of the following reaction? Disregard stereoisomers. b. What is the anticipated percent yield of the major product (as a percentage of all the monobrominated products)?arrow_forwardIn case of dihalide like problem 8.54 c. 1. my think is like this. at the first E2 reaction, the hydrogen on cyclohexyl will be participate because its carbon is more substituted. then second E2 reaction, there are no more hydrogen on left carbon. so hydrogen on right carbon will be partcipate. as a result, the product is double bond not triple bond. Why is this wrong and only form triple bond? 2. Is it impossible to make Sn2 reaction that NH2- is working as nucleophile?arrow_forwardDraw the products of the reaction shown below. Use wedge and dash bonds to indicate stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. 1. Os04 2. NaHSO3, H3O Select to Draw Select to Drawarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
